|
footprint electronics is working on a new type of LCD control concept. The goal is to achieve a high-resolution, high-contrast and color-intensive LCD. A distinction is made between three variants below: 1. LCD Standard 2. LCD Standard High-resolution 3. LCD RGB-Image-dependent (footprint electronics) LCD StandardLCD-Standard use static white light as backlight (BL) to display images. To display 3-color images, RGB-colorfilter are required, which mix a color from the gamut of the backlight. LCD Standard High-resolutionAnother variant of displaying 3-color images on an LCD is to use RGB light as the backlight. With this LCD-control, the colormixing is due to the sequential control of the individual primary RGB-colors of the backlight in combination with the control of the colorless pixels. The result is a high-resolution LCD, since no colorfilter are used. Comparison of both variants:
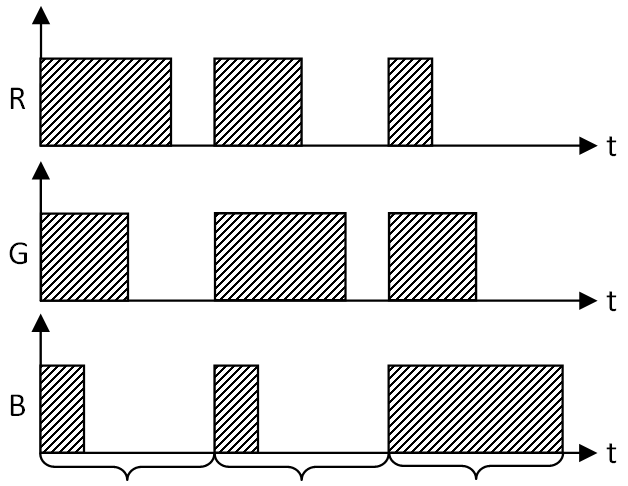
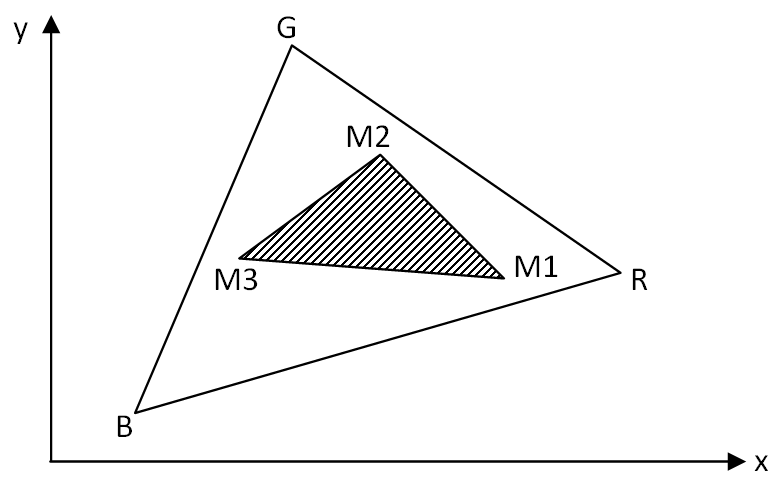
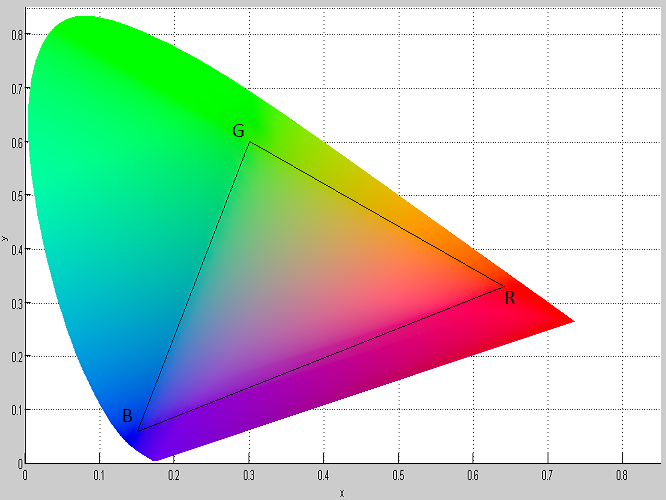
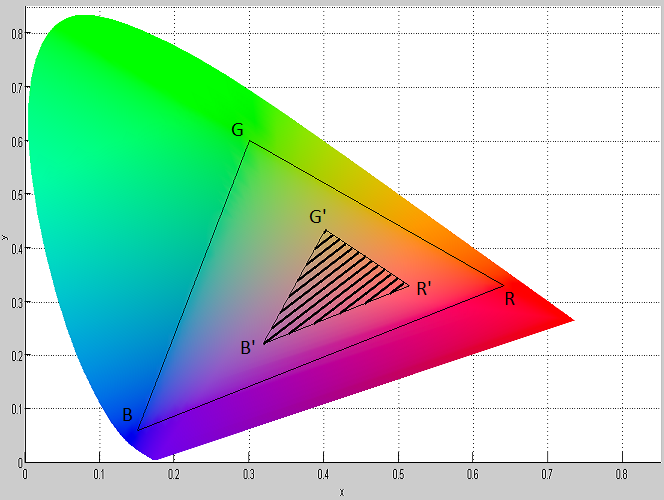
Both LCD-variants have in common that the Xy-color space of the backlight is constant. A constant Xy-color space of the backlight has a negative effect on the image quality in dark images. The aim of the image-dependent LCD-variant is to generate dark images in good quality. This LCD-variant generates a variable Xy-color space of backlight, which can be controlled image-dependent. LCD RGB-Image-dependentBased on the high-resolution LCD-variant, a variable Xy-color space of backlight is generated. This is achieved in three sequential steps by lighting up all three primary RGB-colors at the same time. The ON-time of the RGB-primary colors is individually controlled by using pulse-width-modulation (PWM). Any Xy-chromaticity coordinate from the entire color space of the three primary colors (gamut) can be mixed. Three mixed colors (M1,M2,M3) result in three sequential steps, which span a reduced and image-dependent color-triangle. Figure 1 shows a PWM-control and a resulting color space (M1,M2,M3) from the gamut (R,G,B). Figure 2 shows the color space of an RGB-LED that spans the color-triangle (R,G,B) and a reduced color-triangle (R',G',B') in the gamut (R,G,B). Figure 3 shows the colors of the backlight from the three sequential steps of a LCD-control. Natural images use only a subset of the gamut. In this case only a reduced color-triangle (R',G',B') is required. With the pixel-data of the LCD-pixels, each color from the color-triangle (R',G',B') can be mixed. Features LCD RGB-Image-dependent: 1. Shorter ON-time of the backlight 2. Higher contrast ratio 3. Low energy consumption Another advantage of this backlight is that in addition to RGB-LED, RGB-OLED is also possible as backlight.
Note: Exemplary color spaces Panten application DPMA: 10 2017 004 500.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | LCD-Backlight |